Drug Delivery Methods
What is drug delivery?
Drug delivery is the way in which medications are given to ICU patients. Due to the advances in medicine, drugs may be delivered in many different ways using many different delivery systems including: by mouth (pills or suspensions), through the vein (intravenously), through the artery (arterially), topically through the skin (transdermally), through the rectum (suppository), through the eye (ocular), through the lungs (inhaled), by injection into the skin (subcutaneously), by injection into the muscle (intramuscularly), and under the tongue (sublingually).
Pills or Suspensions
It is common to give ICU patients medications by mouth. Many patients will be able to take pills in the usual fashion. Patients who have feeding tubes in place are usually given their medications through these tubes. Medications may have to be crushed or dissolved in water to be given through these tubes. Some of the medications come in a suspension or liquid from and can be directly given through the tubes or be taken by mouth. Occasionally the patient's stomach or intestines may not work properly and another way to give medications must be found.
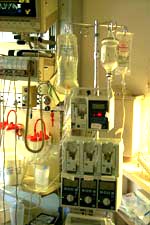
Intravenously
Many of the medications that ICU patients receive must be given intravenously. Medications may be given by "IV push" where the nurse injects the medication directly into the IV line while other medications need to be given more slowly. Medications needing more time to be given may be slowly infused into the patient through a small IV bag (called an IV piggy-back) attached to the main IV line. Some medications and IV fluids need to be given through an IV pump system. The IV pump gives the fluid or medication at a very specific rate and over a very specific time. This prevents the medication or fluid to be given to slowly or to quickly. The IV pumps vary in size and shape. IV pumps have alarms that you may hear.
Arterially
Very few medications are given through the artery in ICU patients. The most commonly used agent given through the artery is called contrast material. This is truly not a medication but rather an agent that is given to outline the artery if damage or blockage of the artery is suspected. This agent is usually given to the patient in the radiology department so that special x-rays of the artery can be taken at the same time.
Transdermally
Several medications are absorbed through the skin. The medication may be in the form of a cream or a patch. These medications may need to be placed on the skin several times a day or only replaced after several days. Nitrogylcerin (used for chest pain), clonidine (used for high blood pressure) and fentanyl (used for pain) are a few examples. Some patients develop skin irritation from this form of drug delivery.
Rectal
Many medications may be absorbed through the mucosa (moist skin) of the rectum. The medications are usually prepared in a wax suppository that melts when given to the patient to allow for slow absorption. The amount of medication that is absorbed is not always predictable. Tylenol is one example of this from of medication.
Ocular
Medications may be delivered directly to the moist covering (conjuctiva) over the eye. These medications are given for eye problems only. Examples include glaucoma and antibiotic eye drops.
Inhaled
Many medications are given directly into the lungs by the inhaled route. These medications frequently act to treat conditions of the lungs. The medications may be given through a hand held inhaler or nebulizer (small machine that produces a mist that includes the medication). These medications are usually used to treat asthma, emphysema, and rarely infections. In an emergency situation, several life saving medications can be given directly into the lungs through a breathing tube.
Subcutaneously
Medications may be given as an injection directly underneath the skin. The medication is slowly absorbed into the body from the tissue just beneath the skin. Two of the most common medications given in this way are insulin (used to treat diabetes) and heparin (used to thin the blood). The absorption of medications through the subcutaneous tissue can occasionally be unpredictable in ICU patients.
Intramuscularly
Medications may be given as an injection directly into the muscle. The medication is slowly absorbed into the body from the muscle. Two of the most common medications given this way to ICU patients are medications to treat pain and nausea (sick to the stomach). Medications given into the muscle are usually associated with pain when injected.
Sublingually
Medications may be given under the tongue and get into the body through the mucosa (moist skin). Because the tongue has a rich blood vessel supply some medications are very well absorbed given this way. The best example is nitroglycerin. This medication is very effective when given sublingually.
Intravenous drug delivery
Pills taken by mouth
