Ultrasound
Ultrasound machines bounce sound waves off body structures and can create very high quality images of certain body parts.
Ultrasound images are commonly used in pregnant women to determine the progress of the pregnancy.
The echocardiogram is an ultrasound image of the beating heart. Information derived from this procedure helps the doctor determine the structure and function of the heart.
Ultra sound images are also commonly made of the gall bladder, pancreas and kidneys.
A type of ultrasound procedure called a duplex ultrasound is also commonly employed to look for blood clots in the deep veins of the legs. The procedure is usually totally painless.
Certain ultrasound devices require placement of the probe into the body. These may be a bit more uncomfortable but are usually tolerated very well. The reason for this is to position the probe as close as possible to the body part of interest. By doing so the image created is often much clearer than if the image were made from the skin surface.
An example of this type of ultrasound imaging is the transesophageal echocardiogram. During this test a probe is placed through the mouth into the esophagus. It is advanced to a position midway between the mouth and stomach. Here the esophagus sits just behind the heart. Because the ultasound probe is so close to the heart, excellent pictures of the beating heart can be obtained.
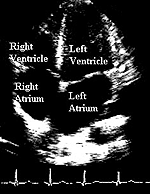 Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiogram)
showing the four chambers of the heart
Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiogram)
showing the four chambers of the heart